A Deep Dive into Task Intensity Manipulation for Athletes
In this article, we'll dive into how to tweak task intensity to ensure the cognitive training plan isn't too easy, setting athletes up for optimal mental sharpness and success.

Manipulating task intensity in cognitive training is the difference between a plan being successful or falling on its face. Just like you'd periodize a workout for strength gains, cognitive tasks must be adjusted and periodized to fine-tune an athlete's cognitive performance. In this article, we'll dive into how to tweak task intensity to ensure the cognitive training plan isn't too easy, setting athletes up for optimal mental sharpness and success.
The Role of Task Intensity Manipulation in Cognitive Training
Every athlete understands that improvement necessitates pushing beyond their comfort zone. This is where the role of task intensity manipulation becomes crucial, ensuring they operate at the optimal level of difficulty.
What is Task Intensity?
Task intensity refers to the cognitive load or mental effort required to perform a specific exercise or task. A practical way to understand this concept is by equating it to the "speed" or "pace" of a task. Just as in physical training, where lifting too light won't yield results, the pace of a task is pivotal in cognitive training. If a task is performed quickly (with short delays between stimuli), it's more intense. Conversely, if the task unfolds at a slower pace (with longer delays between stimuli), it's less intense. This slower pace demands more sustained focus but elicits a less immediate reaction. It's akin to contrasting a sprint with a marathon for the brain: both are challenging, yet they test different capacities.
Why Manipulate Task Intensity? Adjusting task intensity is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Stagnation: Continually working on tasks of the same intensity can lead to plateaus. By manipulating the intensity, athletes can continue to challenge their cognitive abilities.
- Ensuring Progress: Periodizing and adjusting the difficulty ensures that as an athlete's cognitive abilities improve, the tasks evolve to match their new level.
- Maximizing Training Benefits: The right level of intensity ensures that the brain is adequately challenged, leading to better overall cognitive development.
Manipulating task intensity is about finding that sweet spot: challenging enough to promote growth but not so challenging that it becomes overwhelming.
Manipulating Task Intensity
Athletes and coaches understand that a one-size-fits-all approach seldom works. Different athletes have varied goals, and they're at distinct stages in their training, all necessitating tailored strategies. Let's dive into some of the core techniques used to manipulate task intensity in cognitive training:
Undulating Periodisation
Undulating periodisation can be likened to the ebb and flow of the tide. Instead of adhering to a linear progression, this technique involves regular shifts in intensity.
Two Main Models:
Weekly Undulating Periodisation: In this method, the cognitive task intensity changes from week to week. Such an approach guarantees continuous progression, ensuring the training remains invigorating and engaging.
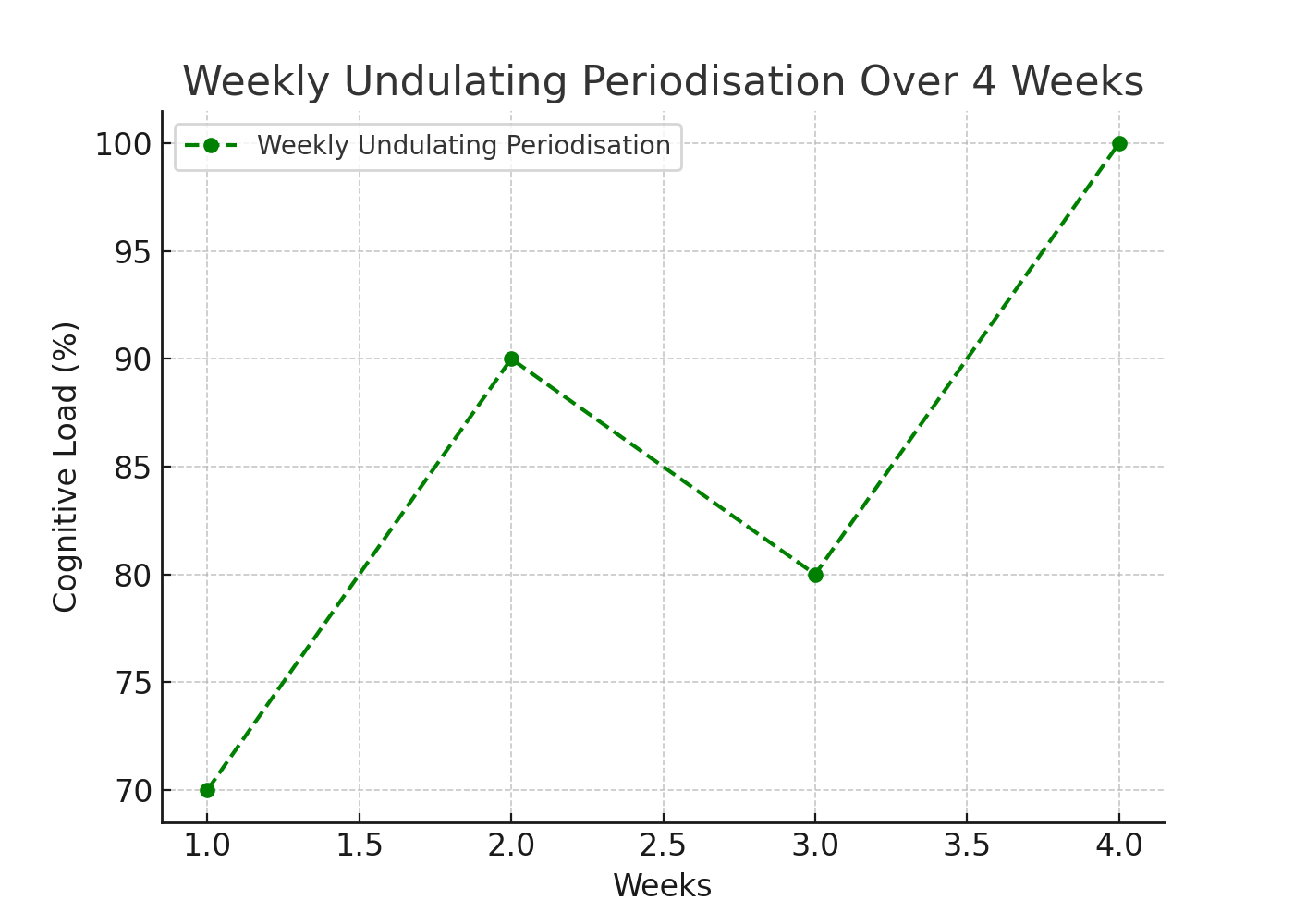
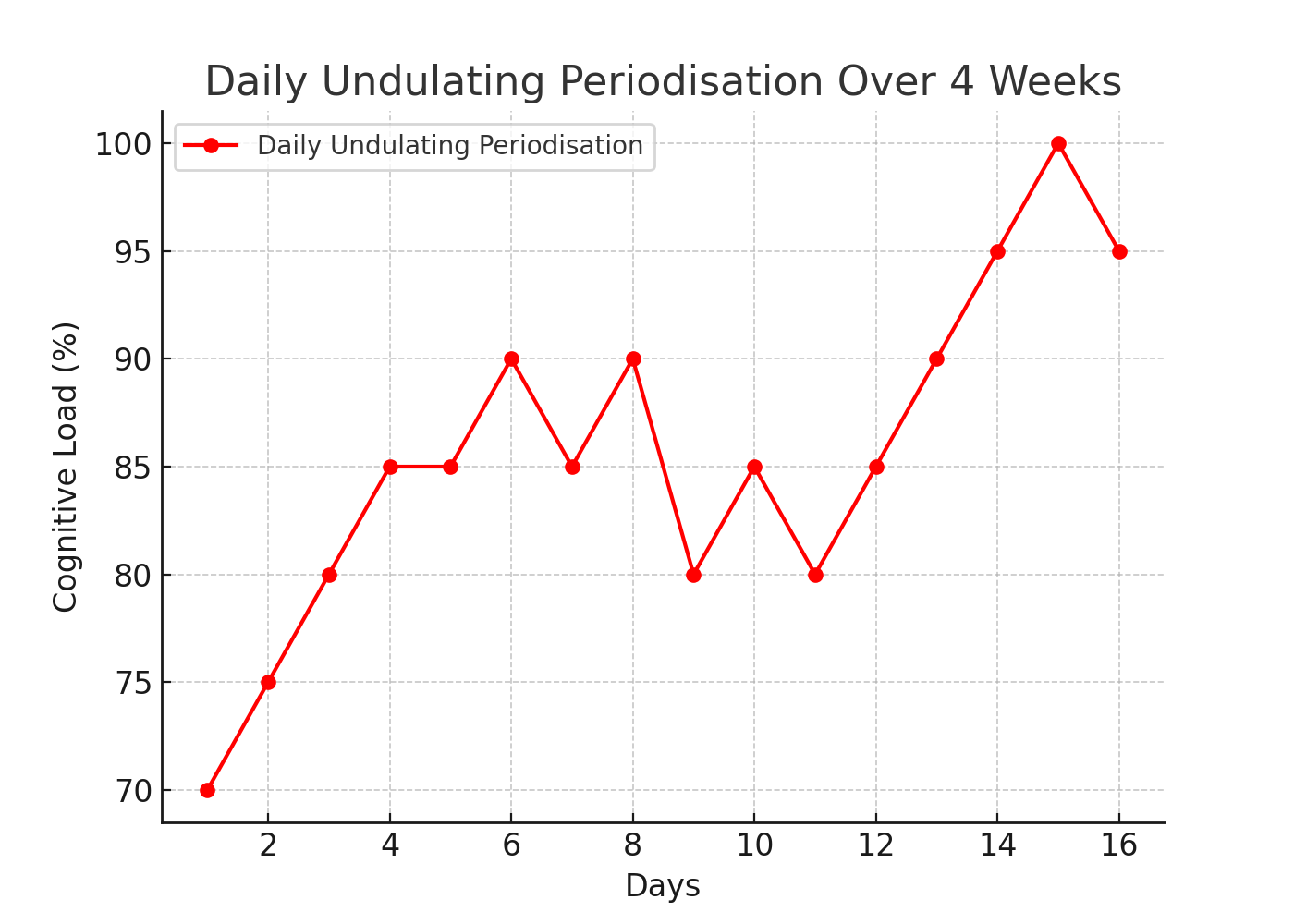
Daily Undulating Periodisation: This strategy entails modifying the task intensity every day. Each day presents a unique challenge, ensuring the athlete stays alert and involved. This daily variation not only bolsters adaptability but also wards off monotony.
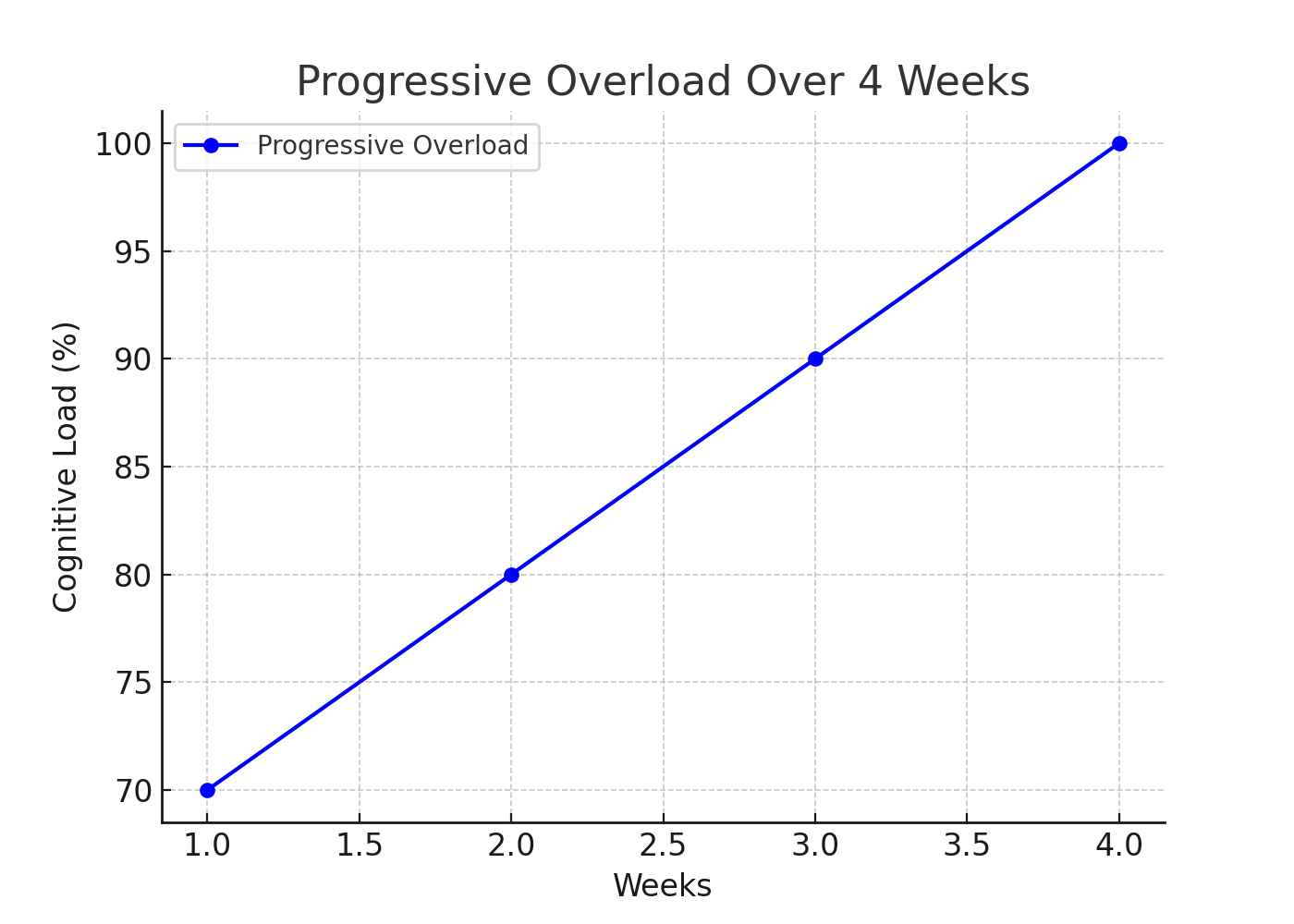
Progressive Overload
Originating from the domain of physical training, progressive overload in cognitive training focuses on steadily and methodically increasing task intensity.
Reducing Task Intensity
While pushing boundaries is essential, there are times when taking a step back is equally important. After intense cognitive efforts, reducing the intensity is imperative for managing the cumulative cognitive load. A decrease in task intensity doesn't suggest that the athlete is easing off. In fact, when faced with lower intensity, athletes frequently realize they must sustain their focus over longer spans. This method can significantly improve their prolonged concentration and hone their response times.
Using Heart Rate Variability (HRV) to Gauge Cognitive Task Intensity
Understanding HRV:Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is the variation in time between successive heartbeats. Rather than being a static measure, like heart rate, HRV offers a dynamic view of the body's response to stress, both physical and mental. In the context of cognitive training, HRV becomes a vital tool to understand an athlete's mental load.
Why HRV Matters in Cognitive Training: Cognitive tasks, just like physical tasks, induce stress. When an athlete is mentally stressed or challenged, it often manifests as changes in their HRV. An optimal cognitive load will generally cause a reduction in HRV, indicating that the brain is working hard and is being adequately challenged.
Monitoring HRV:It's vital to track HRV not just during the task, but also over longer durations. Continuous monitoring of HRV offers insights into how an athlete's body and brain are adapting to the cognitive training regimen. Ensuring the athlete can recover after a session is crucial. While it's necessary to apply sufficient stress to induce adaptations, overextending can hinder recovery, undermining the overall effectiveness of the training.
Interpreting HRV during Cognitive Tasks:
HRV Increasing Over Session: If the HRV is on an upward trend during a cognitive task, it's a potential sign that the task might not be challenging enough. An increase in HRV could indicate that the athlete is relaxed and not mentally taxed. For a training regimen aiming at pushing cognitive boundaries, this isn't ideal.
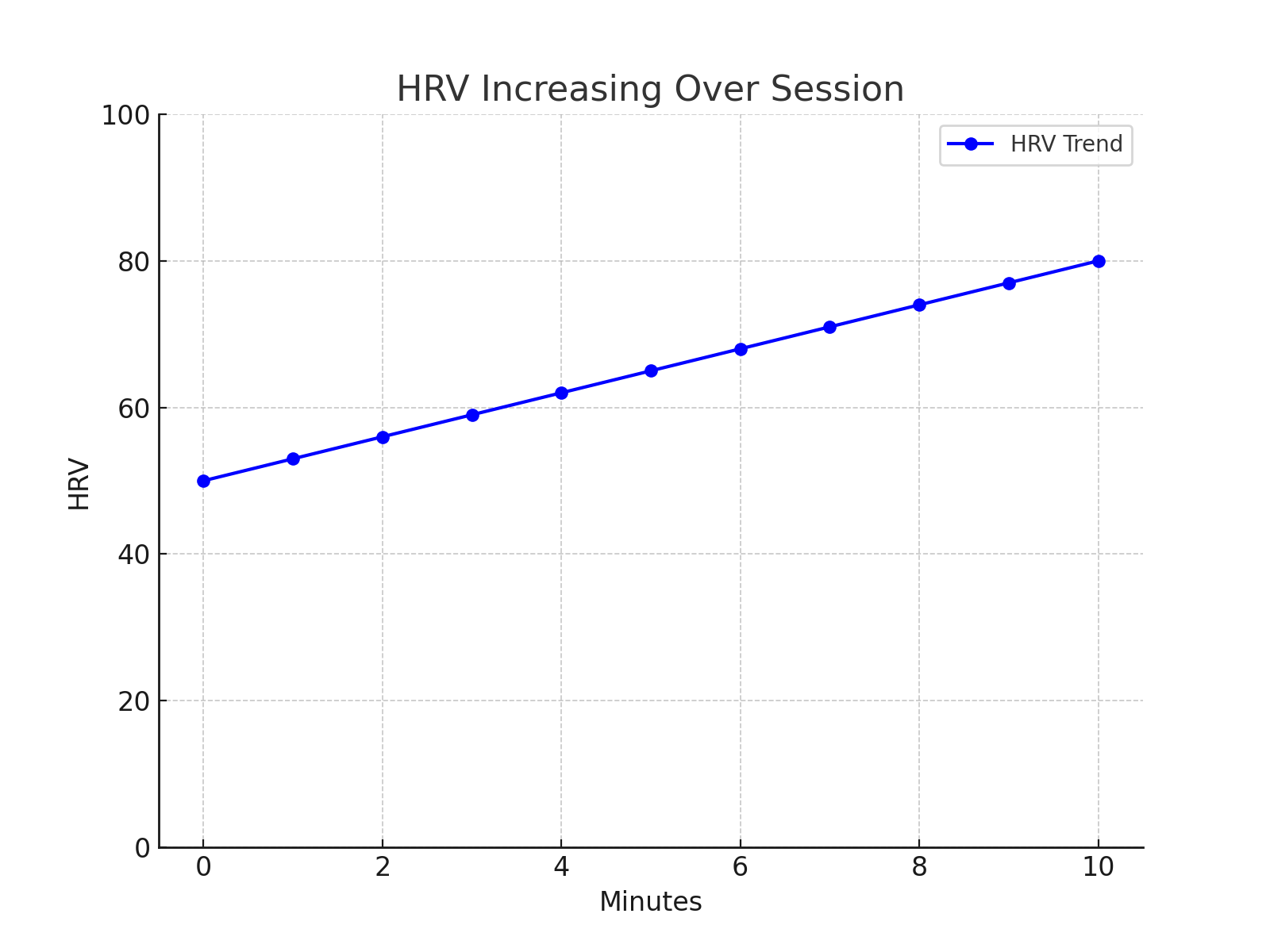
HRV Fluctuating but Trending Downward:
A fluctuating HRV that generally trends downward is indicative of an optimal cognitive load. The fluctuation represents the dynamic nature of the task, while the downward trend signifies that the task is engaging and mentally stimulating.
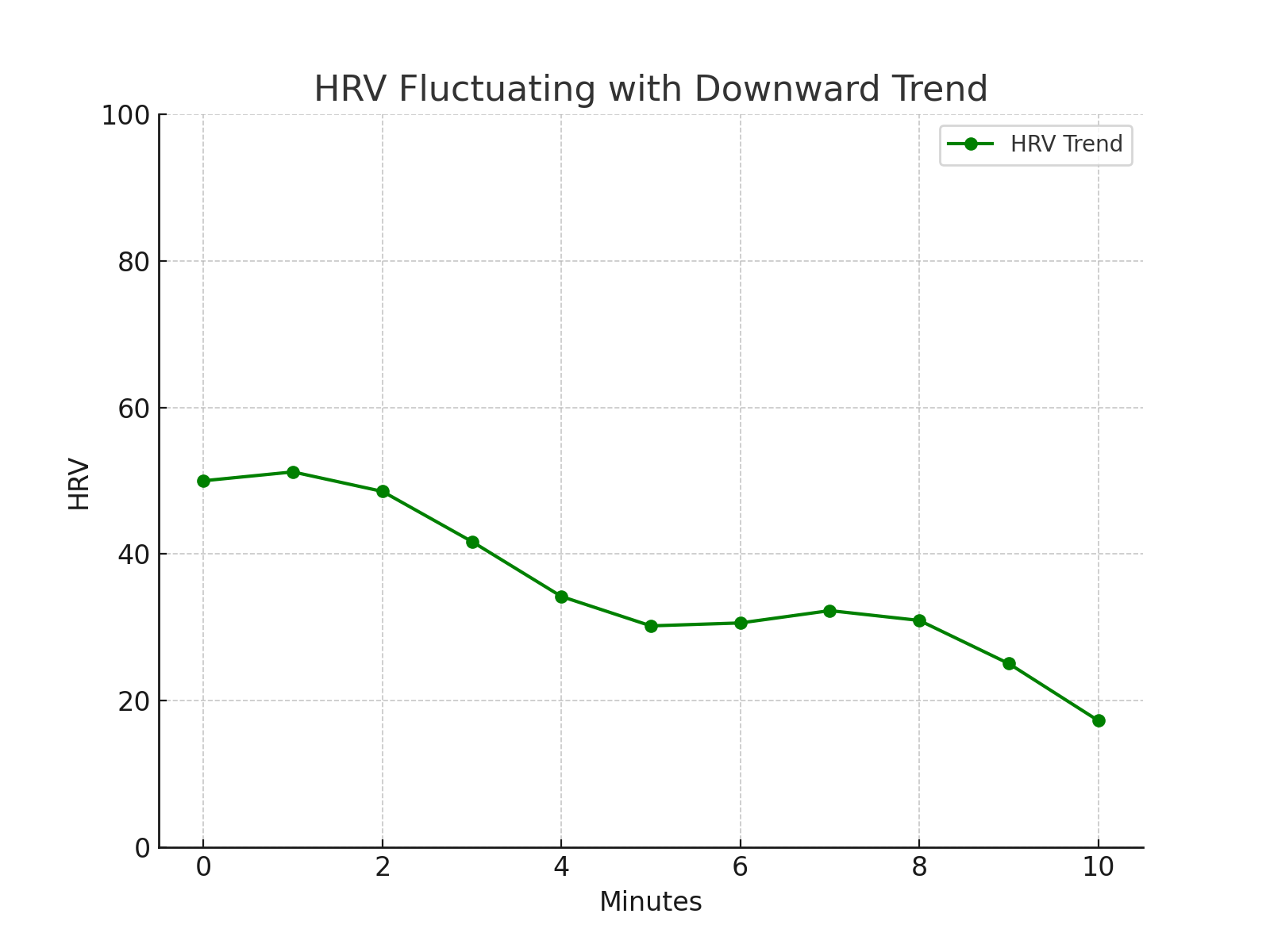
Fine-tuning Task Intensity with HRV:
To harness the full potential of cognitive training, it's essential to utilize data-driven insights. HRV provides real-time feedback on how an athlete's body is responding. If the HRV trends upward consistently, it might be time to increase the task's complexity. Conversely, a sharp downward trend could indicate excessive mental strain, suggesting the need for a lighter task or a break.
Using PVT-B to Gauge Session Intensity
For athletes and coaches, ensuring that each training session hits the right level of intensity is essential. Too light, and the athlete may not be sufficiently challenged. Too intense, and the risk of burnout increases. The PVT-B (Psychomotor Vigilance Task-Brief) test offers a reliable means to strike this balance, acting as a barometer for cognitive load.
Deciphering Mental Fatigue and its Relation to Intensity
Mental fatigue doesn’t merely signify tiredness. It's evident when an athlete's reaction times slow, motivation dwindles, concentration wavers, and 'brain fog' sets in. Such fatigue, often stemming from the cognitive demands of the sport, can indicate whether the training session was intense enough to challenge the athlete.
PVT-B: The Mental Fatigue Indicator
The PVT-B test is a short, three-minute visual reaction assessment that measures an athlete's ability to respond to a stimulus swiftly and accurately. This rapid-response requirement simulates the split-second decision-making scenarios in competitive sports.
Why PVT-B is the Key:
- Pre-training: A baseline PVT-B test determines an athlete's initial mental fatigue levels.
- Post-training: Another PVT-B test gauges the mental fatigue resulting from the training session.
If an athlete's post-training PVT-B scores (like reaction time and lapse count) deteriorate, it suggests that the session was intense enough to challenge their cognitive capacities.
Reading Between the PVT-B Lines
Key PVT-B indicators include:
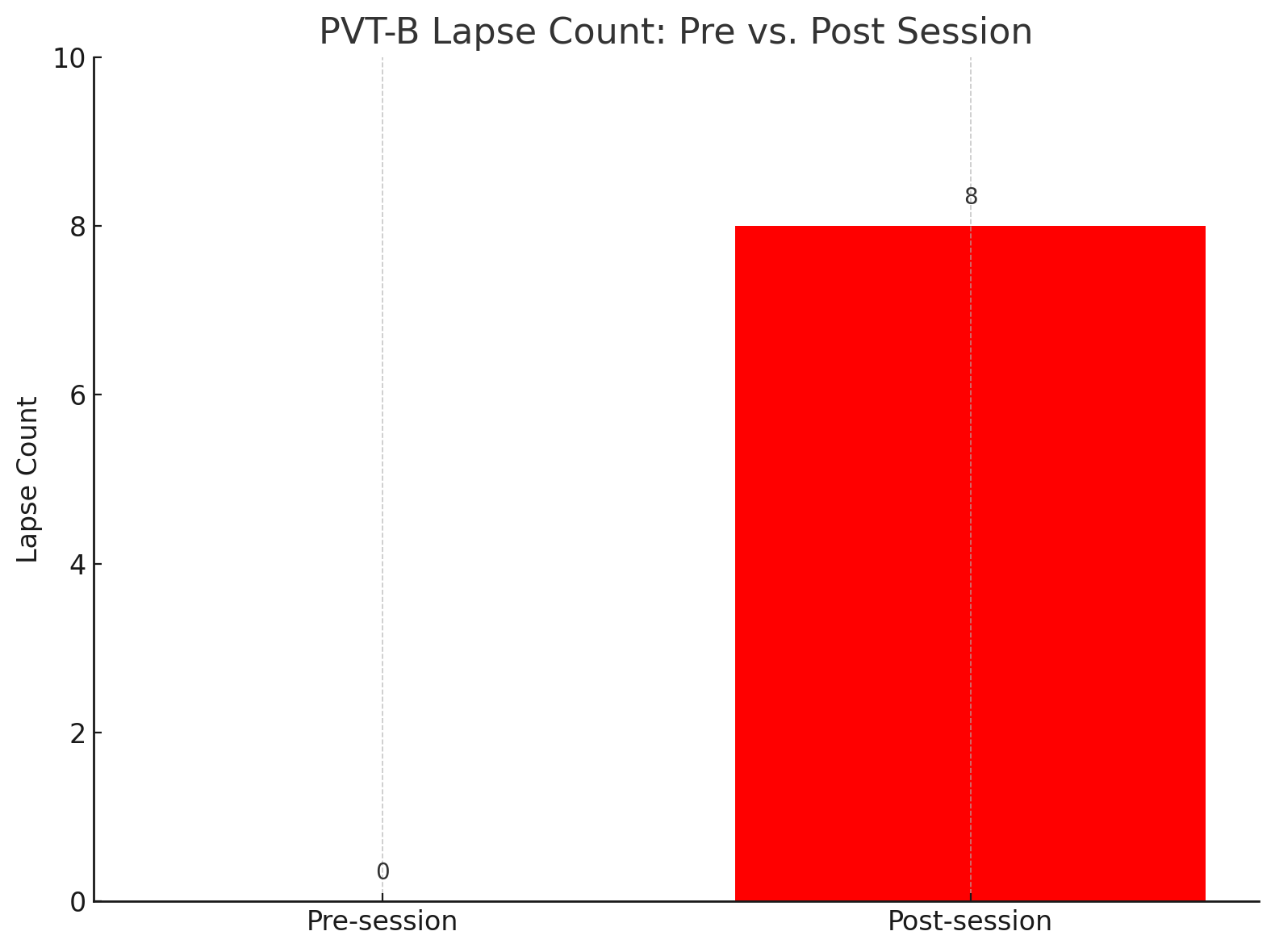
Lapse Count: An increase in lapse count (extremely slow responses) post-training indicates heightened mental fatigue, suggesting an adequately challenging session.
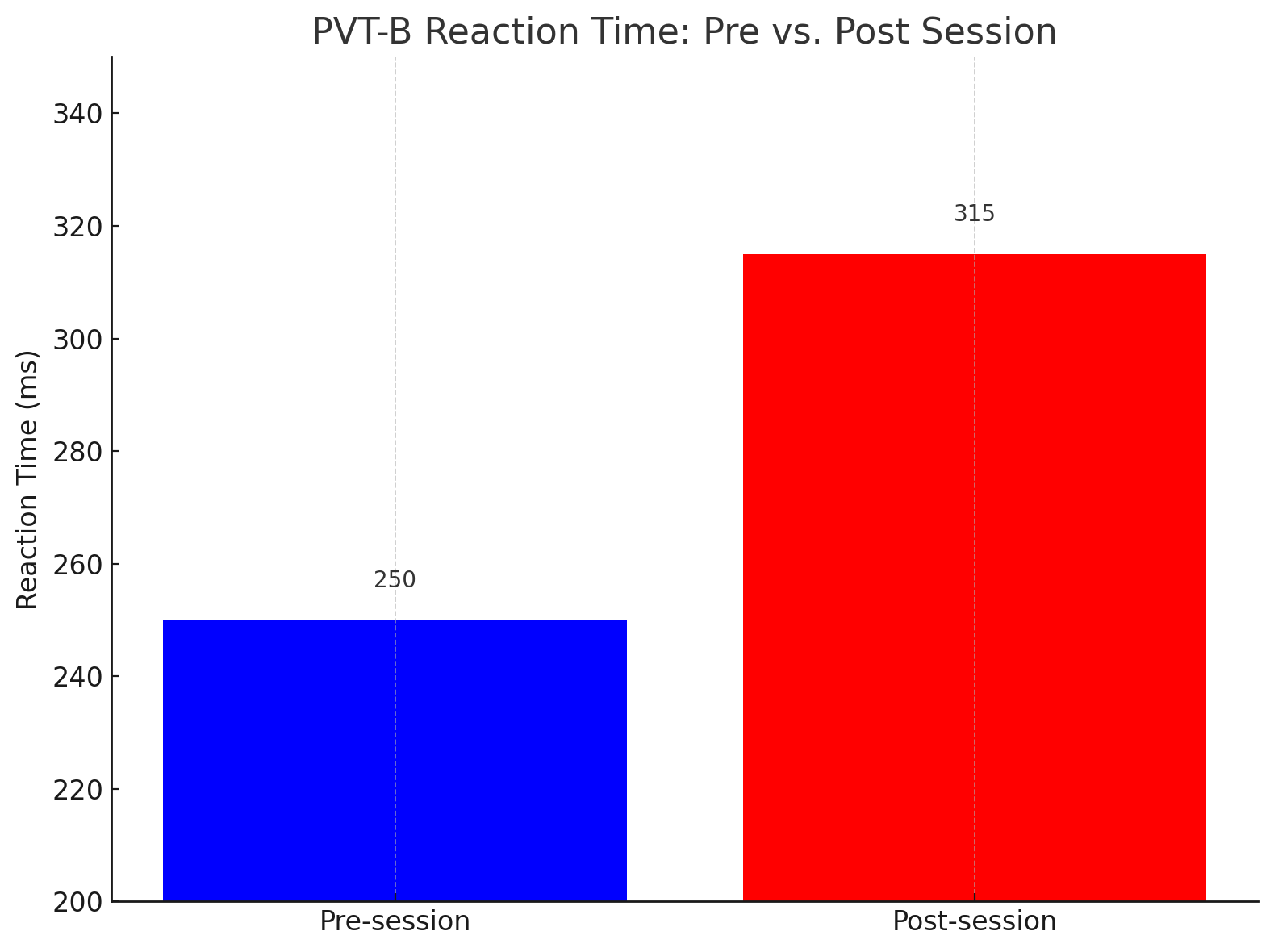
Reaction Time: Slower post-training reaction times further confirm that the training was intense enough to tax the athlete's cognitive capabilities.
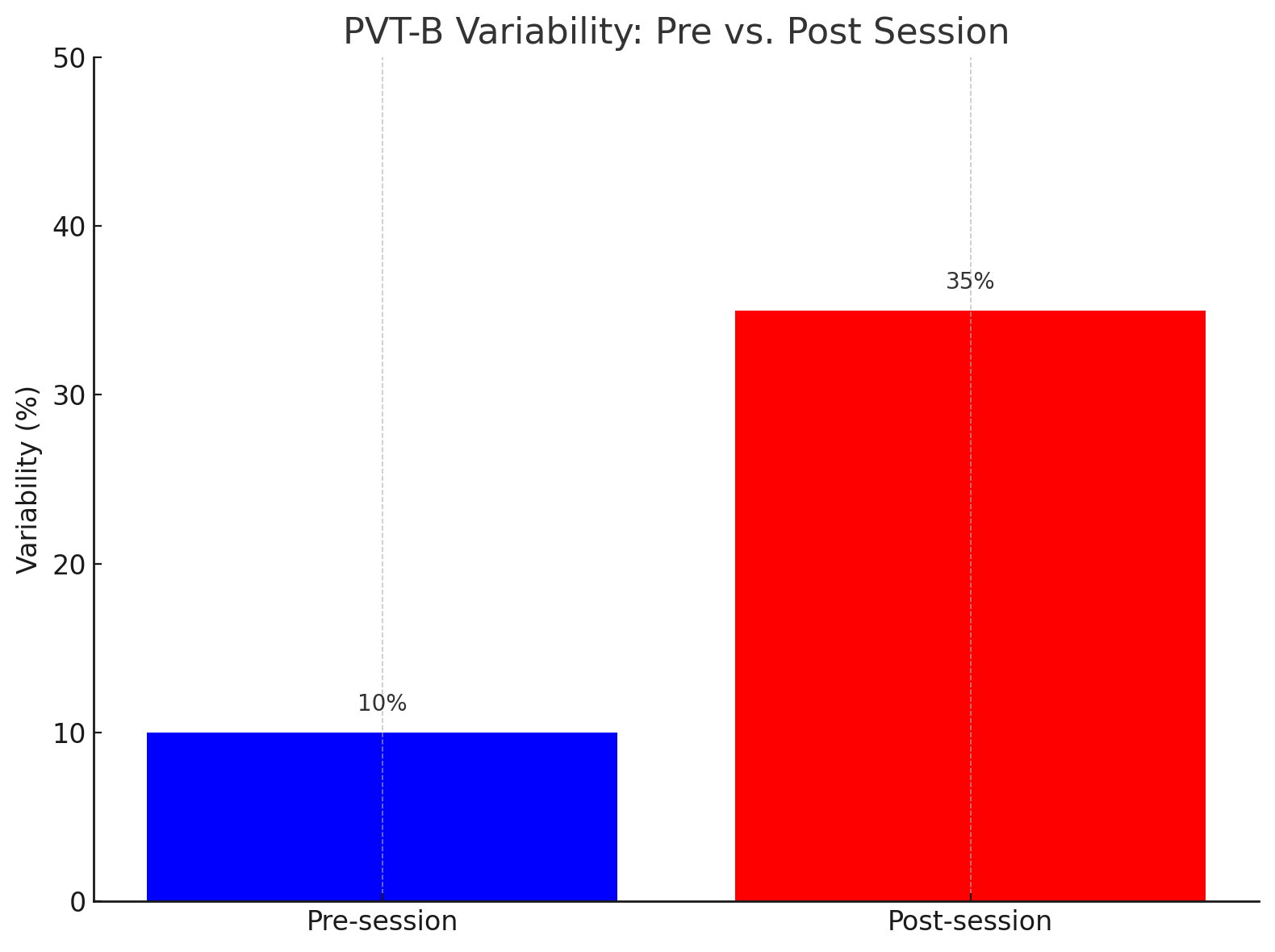
Variability: Greater variability in responses post-training suggests decreased focus, another sign of an effective, intense session.
Adjusting Training Intensity Using PVT-B Insights
These PVT-B test results inform subsequent training sessions. For instance, consistently deteriorating PVT-B scores before training sessions might indicate cumulative fatigue and the need for recovery or reduced intensity. On the other hand, if there's little change in PVT-B scores before and after a session, it could suggest the need to ramp up the intensity.
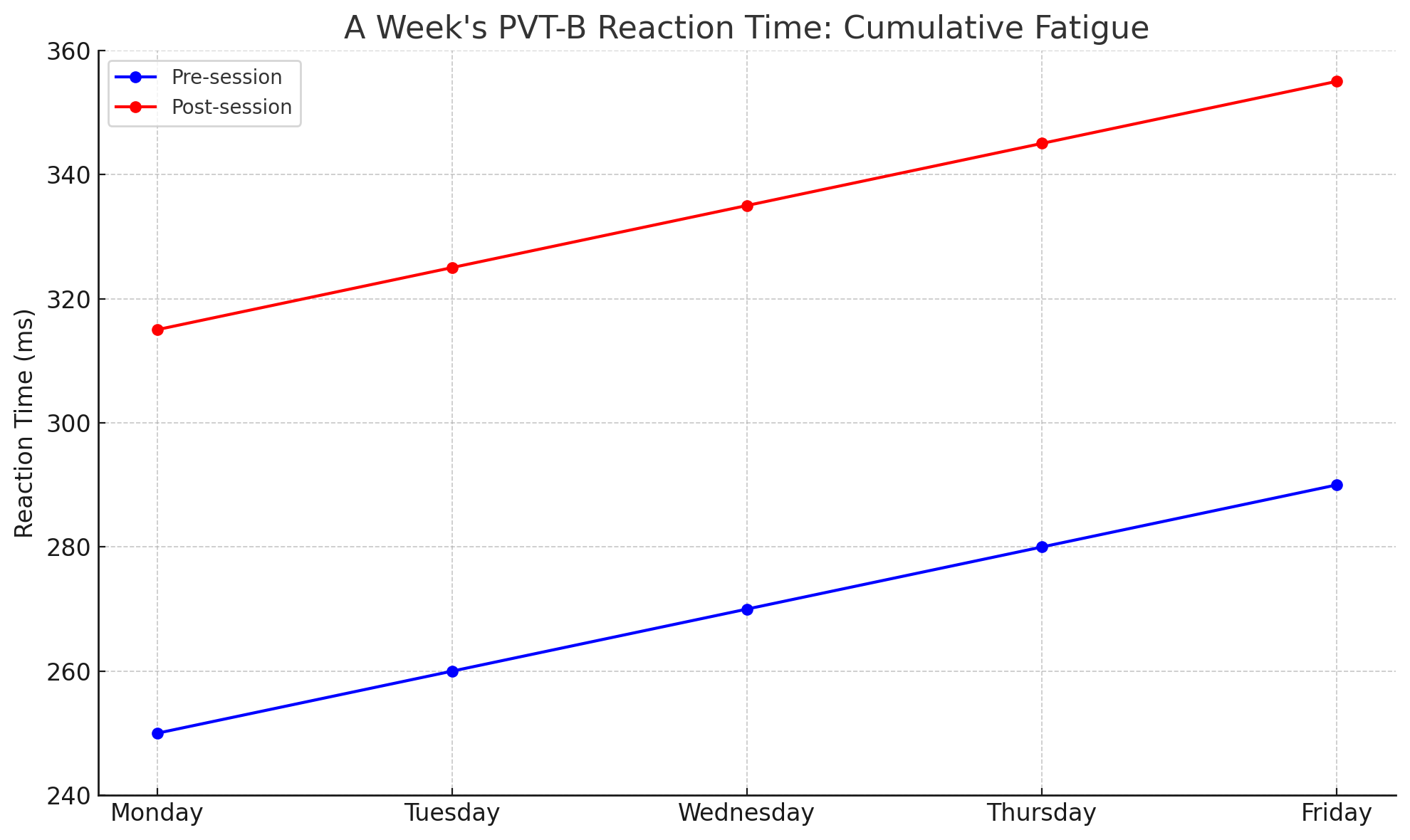
Harnessing the PVT-B test as part of an athlete's cognitive training routine offers a clear advantage: the ability to adjust session intensities based on real-time data. This ensures that athletes are consistently challenged but not overwhelmed, paving the way for optimal performance. In cognitive training, where intensity is both an art and a science, the PVT-B test stands out as an invaluable tool.
Fine-Tuning Cognitive Performance with Precision
In an era where sports performance hinges not just on physical capabilities but also on cognitive performance, understanding and optimizing task intensity is the game-changer. Through consistent monitoring, data-driven insights, and a nuanced understanding of each athlete's unique cognitive profile, success in cognitive training is not just achievable—it's inevitable.
🌐 Connect With Us
🌍 Soma Technologies: Engineered to enhance human performance.
📸 Instagram: Dive into our world through exclusive photos and stories.
👥 Facebook: Join our community for the latest updates and discussions.
📈 LinkedIn: Connect with us professionally and stay informed about industry news.
🎥 YouTube: Watch our latest videos, tutorials.
🐦 X: Follow us for instant updates, news, and engaging tweets.
